What Is WebRTC Used For? Does WebRTC Leak Your IP Address?
Take a Quick Look
Discover what WebRTC does, its real-world uses, IP leak risks, and how AdsPower protects your privacy with advanced WebRTC modes. Stay secure—try AdsPower today.
Real-time communication has become a foundational part of the modern web—powering everything from browser-based video calls to telemedicine, online gaming, and customer support. At the center of all this is WebRTC, a technology that enables instant audio, video, and data exchange directly in your browser.
If you've ever used Google Meet, Discord, online classrooms, or even live customer support windows on big platforms, you've already relied on WebRTC without realizing it. But as WebRTC becomes more widely used, so do concerns around IP exposure, device fingerprinting, and online identity tracking.
Why WebRTC Is Essential Today?
Since our previous article already explained WebRTC's technical fundamentals, we'll skip the "what is WebRTC" basics and go straight into what users really search for today.
At its core, WebRTC enables real-time, peer-to-peer (P2P) communication between browsers and applications. This bypasses centralized servers and minimizes latency. Because of that, WebRTC is now embedded in many tools people use daily—often invisibly.

What Is WebRTC Used For? The Real-World Applications
WebRTC powers a wide range of modern online experiences. Here are the most common and important use cases.
Video Conferencing and Collaboration Tools
Most browser-based video platforms run on WebRTC because it offers low latency and doesn't require users to install an app. Well-known examples include:
- Google Meet
- Discord
- Slack's browser-based calls
- Microsoft Teams (browser version)
- Whereby
- ClassDo and other education platforms
These services rely on WebRTC for video streaming, audio synchronization, screen sharing, and real-time collaboration.
Telemedicine and Online Healthcare
Security and encryption are essential in telemedicine. Platforms like Doxy.me, Amwell, and other HIPAA-compliant services use WebRTC because it supports end-to-end encrypted video sessions directly in the browser.
Doctors can consult patients securely—no software installation required.
Cloud Gaming and Low-Latency Streaming
Real-time gaming and cloud streaming demand ultra-low latency. WebRTC offers precisely that.
- NVIDIA GeForce NOW
- Google Stadia (technology now used across Google Cloud)
- Interactive livestream platforms like YouTube Live and Twitch
Even when viewers interact with streamers (co-streaming, voice chat, two-way events), WebRTC handles the real-time component.
Online Education and Remote Learning
Many e-learning tools use WebRTC for virtual classrooms, breakout rooms, and instant teacher–student communication:
- Google Classroom video calls
- Online tutoring platforms
- Virtual training and onboarding tools
The ability to run in any browser makes it ideal for large-scale virtual learning environments.
Customer Support, Sales Calls & Identity Verification
When you click "Talk to a live agent" on websites like Airbnb or major banks, the resulting audio/video session is often powered by WebRTC.
Customer verification tools also use WebRTC for webcam-based identity checks, KYC verification, and biometric capture.
Bottom line:
WebRTC is everywhere—video, audio, gaming, education, customer support, and browser-based communication. Its usage continues to expand, but so do the privacy concerns associated with it.
The Hidden Issue: WebRTC Fingerprinting and IP Exposure
While WebRTC delivers speed and convenience, it also unintentionally exposes sensitive device and network details.
This is why searches like:
- "Is WebRTC leaking my IP address?"
- "Does WebRTC expose my real location?"
- "Is WebRTC safe for multiple accounts?"
have surged in recent years.
Let's break down what's actually happening.
What Data WebRTC Reveals by Default
WebRTC was designed to make network routing efficient, not anonymous. To establish a direct connection, your browser must share network details including:
- Your public IP address (the one shown to the internet)
- Your local IP address (your device's internal network identity)
- Your device's network interfaces (Wi-Fi, Ethernet, etc.)
Media device identifiers (camera and microphone IDs)
When these details are combined with your browser info, OS version, hardware characteristics, and other technical parameters, websites can generate a unique fingerprint of your device—even if you're using a VPN.
Why WebRTC Reveals IP Addresses
To establish the fastest P2P route, browsers exchange internal and external IP addresses using STUN/TURN servers. Fingerprinting scripts take advantage of this process.
Key point:
Your browser may leak your IP address even if you never make a video call.
A simple WebRTC script embedded in the page can extract the IP information silently.
Does WebRTC Leak Your IP Address?
The short answer: Yes—unless you take steps to prevent it.
Here's how WebRTC leaks typically happen:
Public IP Leaks
WebRTC can reveal your public IP address—even when behind a VPN—if the VPN doesn't fully handle WebRTC leak protection. Some VPNs only route regular browser traffic, not WebRTC queries.
This is especially problematic for:
- Social media marketers
- Multi-account managers
- Affiliate marketers
- eCommerce managers
- Anyone trying to maintain separate digital identities
Local IP Leaks
WebRTC also exposes your local network IP, which reveals:
- Your device's internal network structure
- Whether you're on Wi-Fi or Ethernet
- Your network interface ID
Local IP information is extremely valuable for fingerprinting systems used by ad networks, anti-fraud tools, and social platforms.
Fingerprinting Before the Connection Even Starts
Websites don't need you to join a video call. Fingerprinting scripts can pull WebRTC data during page load—before any permission request appears.
This means:
- Your identity can be matched across multiple accounts
- Anti-fraud systems can detect "same user, different account"
- Websites can identify your true IP location even behind proxies
This is why professional users increasingly rely on tools like AdsPower that simulate or block WebRTC behavior without breaking website functions.
How to Prevent WebRTC IP Leaks (Practical Methods)
Here are the most effective approaches to preventing WebRTC exposure.

Disable WebRTC (Limited Use)
Some browsers (like Firefox) allow WebRTC to be disabled manually. For Chrome-based browsers, users need third-party extensions.
Major drawback:
Disabling WebRTC breaks video calls, voice chats, and any site that depends on it.
This solution is only suitable for users who never need real-time browser communication.
Use a VPN with WebRTC Leak Protection
A VPN can hide your public IP from WebRTC—but not always your local IP. Many VPNs block only part of the WebRTC process. As a result, fingerprinting systems may still identify your device.
This approach helps, but it's not foolproof.
Use an Antidetect Browser with WebRTC Protection (Recommended)
Privacy-centric browsers like AdsPower give users full control over WebRTC behavior. This is the most effective method for:
- Multi-account management
- Avoiding fingerprint correlation
- Masking real IP and device information
- Maintaining separate identities safely
- Working with ad platforms, eCommerce platforms, and social media accounts
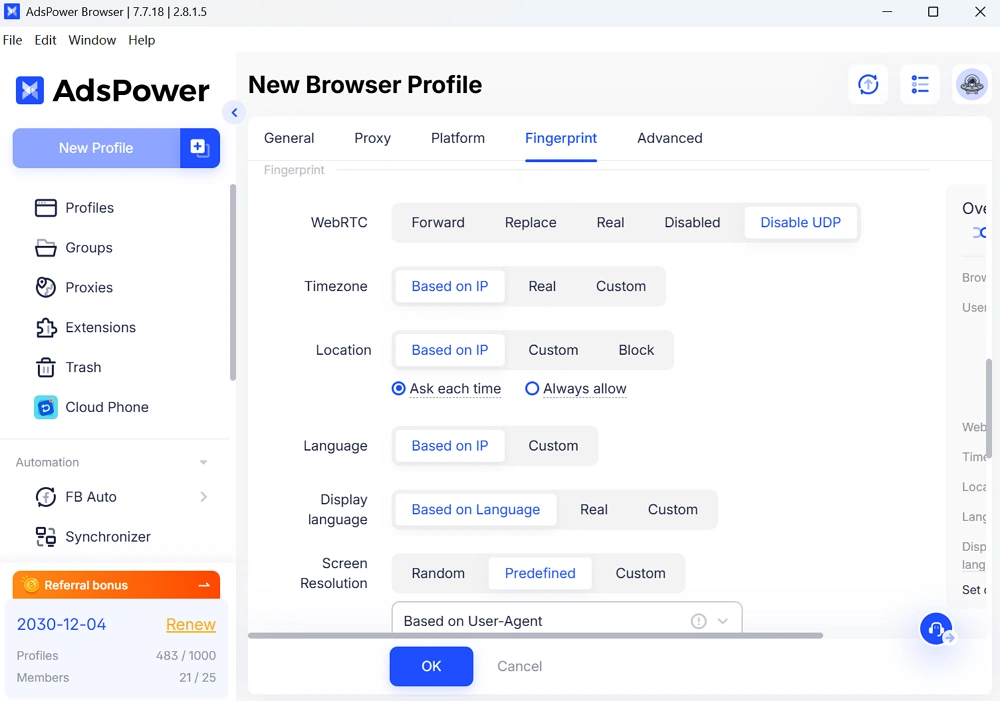
AdsPower Advanced WebRTC Protection Modes
AdsPower browser offers multiple WebRTC modes, each designed for specific use cases. Unlike simple browser extensions, AdsPower controls WebRTC at the network and environment level, providing far more robust privacy protection.
Here's a breakdown of each mode.
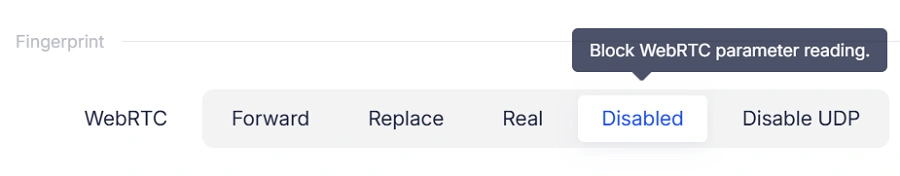
Disable Mode
- Completely disables WebRTC
- But instead of blocking the browser API (which websites can detect), AdsPower intercepts traffic
- Websites interpret the block as a firewall or network restriction
- Prevents all WebRTC fingerprint leaks
Best for:
Users who don't need WebRTC functionality and want maximum privacy.
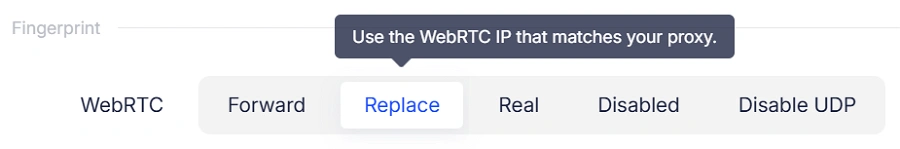
Replace Mode
- WebRTC remains functional
- But all IP and fingerprint information is replaced with environment-matched fake data (e.g., consistent with your proxy IP)
- Websites see realistic fingerprints, not your true identity
Best for:
Avoiding account linkage while maintaining normal WebRTC behavior.
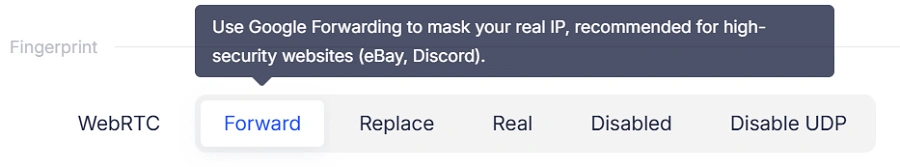
Forward Mode
- A stronger version of Replace Mode
- Forces all WebRTC server requests to go through Google's public WebRTC servers
- Prevents websites from using self-hosted STUN servers to detect your true IP
Best for:
Ad platforms, eCommerce platforms, and websites with advanced anti-fraud systems.
Disable UDP Mode (New)
The modes above can prevent fingerprint leaks, but they may also break websites that rely on WebRTC. The new "Disable UDP" mode solves this issue by keeping essential WebRTC functions available without exposing your real IP.
- Blocks only the UDP channels used by WebRTC
- Prevents WebRTC from using UDP paths that could reveal your real IP (since UDP can bypass the browser's proxy settings)
Because the browser proxy works over TCP, blocking UDP ensures WebRTC cannot fall back to any direct UDP route that would expose your actual network IP.
This allows:
- Video calls and real-time features to continue working
- All traffic to follow your configured proxy settings
- Your real IP stays protected
Works well with:
Google Meet, TikTok, major live platforms
Best for:
Users who need WebRTC functions without revealing their real IP.

Which WebRTC Mode Should You Use? (Quick Guide)
|
User Need |
Recommended AdsPower Mode |
|
Maximum privacy, no WebRTC needed |
Disable Mode |
|
Need WebRTC functions + IP protection |
Disable UDP Mode |
|
Avoid account linkage + realistic fingerprint |
Replace Mode |
|
Advanced anti-detection environments |
Forward Mode |
Final Thoughts
WebRTC is essential to the modern internet, powering everything from video calls to cloud gaming. But its default behavior can expose sensitive information—even when you're using a VPN.
If you manage multiple accounts, work in digital marketing, or simply value your privacy, you must control how WebRTC behaves in your browser.
Tools like AdsPower offer the most flexible, secure, and user-friendly WebRTC protection available today—allowing you to stay anonymous without sacrificing functionality.
Stay protected. Choose the WebRTC mode that fits your workflow.

People Also Read
- Top Tools to Prevent Account Bans by Ensuring Consistent Browser Environments (2026 Guide)

Top Tools to Prevent Account Bans by Ensuring Consistent Browser Environments (2026 Guide)
If you are looking for the best tool for preventing account bans with consistent browser environments, don't miss such a practical guide
- Browser Consistency & Kernel Mismatch: Why Accounts Get Banned (2026)

Browser Consistency & Kernel Mismatch: Why Accounts Get Banned (2026)
Avoid bans caused by fingerprint mismatches. Learn how AdsPower syncs browser cores, TLS, Canvas, and WebGL signals for consistent profiles in 2026.
- How Browser Fingerprinting Triggers Account Locks (And How AdsPower Prevents Them)

How Browser Fingerprinting Triggers Account Locks (And How AdsPower Prevents Them)
How browser fingerprint mismatches cause account locks & how AdsPower's dual-engine architecture with real browser cores & Native Mobile Simulation pr
- 8 Best Whoer Alternatives in 2026 ( Accurate & Private IP Check Tools)

8 Best Whoer Alternatives in 2026 ( Accurate & Private IP Check Tools)
Looking for a Whoer.net alternative? Discover our 2026 list of the 8 best IP check tools for accurate, private fingerprint analysis and enhanced onlin
- What is BrowserScan? Check Fingerprints, IP Leaks & Stay Private

What is BrowserScan? Check Fingerprints, IP Leaks & Stay Private
What is BrowserScan? Find out how it detects IP leaks & unique fingerprints, plus tips for privacy with AdsPower.


