Types of Browsers in 2026: Popular Web Browsers and Advanced Browser Types
Take a Quick Look
Are you wondering what difference types of web browsers? Take a look on the detailed comparison based on the different dimensions, and learn how to choose the best for your case.
By 2026, web browsers have evolved far beyond simple tools for opening websites. They now play a critical role in privacy protection, digital identity management, cross-device access, and even business automation. As a result, users are no longer choosing a browser, but selecting from different types of browsers based on how they work, where they run, and what problems they solve.
This guide explains types of browsers, breaks down various types of browsers by category, and answers common questions such as how many types of browsers exist today and what are the different types of web browsers you should consider in 2026.

What Is a Web Browser?
A web browser is a software application that allows users to access, retrieve, and interact with content on the internet. It communicates with web servers using protocols such as HTTP and HTTPS, interprets web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, and displays content in a readable and interactive format.
In 2026, modern browsers do much more than load web pages. They handle:
- User authentication and session management
- Cookies, local storage, and caching
- Security features such as sandboxing and encryption
- Extensions, add-ons, and web applications
- Cross-device synchronization and cloud integration
Because of these expanded responsibilities, types of internet browsers have diversified to meet different technical, personal, and professional demands.
How Many Types of Browsers Are There?
There is no single, universally accepted number. When people ask how many types of browsers exist, the answer depends on how browsers are categorized. In practice, browsers can be grouped by:
- User interface design
- Operating platform
- Core function and use case
- Underlying browser engine
These categories overlap, which is why discussions about various types of browsers often reference multiple classification systems rather than a fixed list.
Types of Browsers Based on User Interface
Graphical User Interface (GUI) Browsers
GUI browsers are the most widely used browsers in the world. They provide a visual interface that supports images, videos, animations, and interactive elements. Features typically include:
- Tabs and windows
- Menus and icons
- Mouse, keyboard, and touch input
GUI browsers dominate both desktop and mobile environments and are the default choice for everyday users, businesses, and students.
Text-Based Browsers
Text-based browsers display web content primarily as plain text, without images or advanced styling. While uncommon for mainstream users, they are still valuable in specific scenarios:
- Low-bandwidth or limited hardware environments
- Terminal-based systems and servers
- Accessibility testing and HTML debugging
Although niche, text-based browsers remain part of the broader ecosystem of different types of web browsers.
Types of Web Browsers Based on Platform
Desktop Browsers
Desktop browsers run on operating systems such as Windows, macOS, and Linux. They are typically the most powerful and flexible browsers available, offering:
- Full-featured developer tools
- Extensive extension ecosystems
- Multi-profile and session management
Desktop browsers are widely used for professional work, software development, research, and content creation.
Mobile Browsers
Mobile browsers are optimized for smartphones and tablets. Their design prioritizes:
- Touch-based navigation
- Performance on limited hardware
- Battery and data efficiency
Many mobile browsers integrate tightly with operating systems, supporting features such as biometric authentication and system-level sharing.
Embedded and Smart Device Browsers
Embedded browsers are built into smart devices, including:
- Smart TVs
- Vehicle infotainment systems
- Kiosks and IoT devices
These browsers often use simplified interfaces and lightweight engines, focusing on stability and efficiency rather than customization.
Types of Browsers Based on Function and Use Case
Standard Web Browsers
Standard web browsers are designed for general-purpose internet use. Their main goals are speed, compatibility, and ease of use. They support:
- Most modern web standards
- Streaming media and web apps
- A balance between usability and security
For most people, standard browsers are sufficient for daily browsing, work, and entertainment.
Privacy-Focused Browsers
Privacy-focused browsers address growing concerns around online tracking, data collection, and online scams. In addition to blocking third-party trackers and ads, many modern privacy browsers actively identify malicious domains and take down fake websites to protect users from phishing attacks, fraud, and credential theft. They typically include features such as:
- Blocking third-party trackers and ads
- Limiting cookie-based profiling
- Reducing browser fingerprinting
These browsers are popular among users who want more control over their personal data without significantly changing their browsing habits.
Secure and Anonymous Browsers
Secure and anonymous browsers are built for users who prioritize anonymity and protection from surveillance. They may:
- Route traffic through encrypted or decentralized networks
- Mask IP addresses and locations
- Isolate sessions to prevent tracking
Such browsers are commonly used by journalists, researchers, activists, and users in regions with restricted internet access.
Antidetect Browsers (Advanced Category)
Antidetect browsers represent one of the most advanced types of browsers in 2026. They are specifically designed to manage and isolate multiple digital identities within a single system.
Typical use cases include:
- Multi-account e-commerce operations
- Affiliate and performance marketing
- Social media management at scale
- Automation, testing, and quality assurance
A well-known example in this category is AdsPower, which is widely used by marketing teams and agencies to safely operate hundreds or even thousands of browser profiles without account linkage.
Unlike standard or privacy browsers, antidetect browsers ensure that each browser profile behaves like a completely separate device.
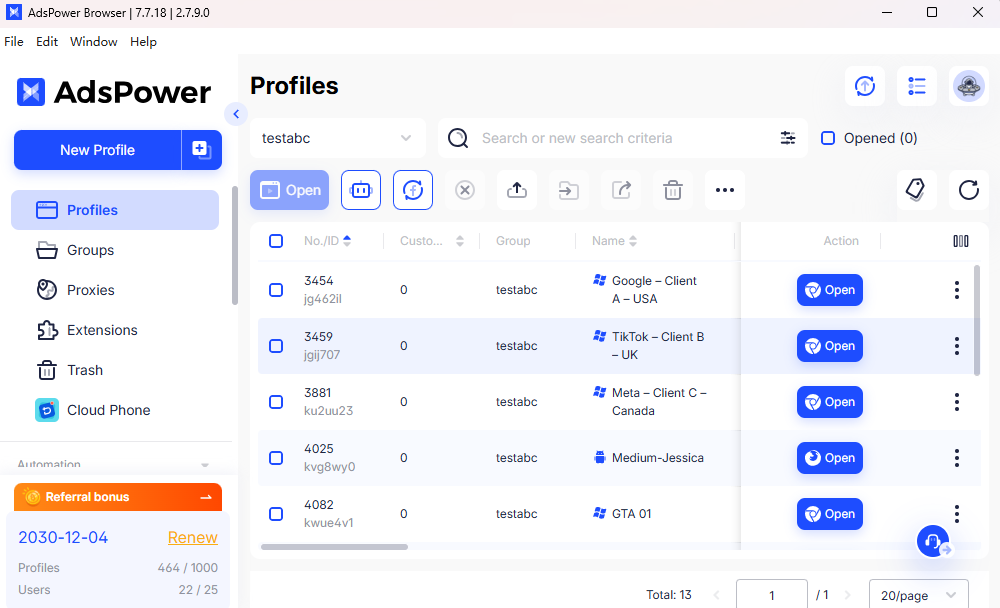
How Antidetect Browsers Work
Antidetect browsers achieve identity isolation by controlling browser fingerprint data. Each profile can have unique parameters such as:
● Operating system and browser version
● Screen resolution, fonts, and time zone
● WebGL, Canvas, and AudioContext fingerprints
● Cookies, cache, and local storage

When combined with dedicated proxies, tools like AdsPower allow each profile to operate independently, significantly reducing the risk of detection, account bans, or cross-account association, something traditional browsers were never designed to handle.
Types of Browsers Based on Engine
Chromium-Based Browsers
Chromium-based browsers use the open-source Chromium engine. They are known for:
- High compatibility with modern websites
- Rapid adoption of new web standards
- Large extension marketplaces
Because many websites are optimized for Chromium, these browsers dominate the global market share.

Gecko-Based Browsers
Gecko-based browsers rely on Mozilla’s independent rendering engine. Key characteristics include:
- Strong focus on privacy and transparency
- Open standards advocacy
- Reduced reliance on Chromium
They appeal to users who value diversity in the browser ecosystem.
WebKit-Based Browsers
WebKit-based browsers are commonly found on Apple devices and embedded systems. Their strengths include:
- Energy efficiency
- Tight integration with hardware and OS features
- Smooth performance on constrained devices
Different Types of Browsers Compared
To better understand the landscape of different types of browsers in 2026, it helps to compare them side by side across multiple criteria instead of only looking at their main purpose. The table below provides a more detailed comparison between standard browsers, privacy-focused browsers, and antidetect browsers, highlighting their strengths, limitations, and ideal use cases.
|
Criteria |
Standard Web Browsers |
Privacy-Focused Browsers |
Antidetect Browsers |
|
Primary purpose |
General internet browsing |
Reduce tracking and data collection |
Isolate and manage multiple digital identities |
|
Typical users |
Everyday users, offices, students |
Privacy-conscious individuals |
Marketers, agencies, developers, automation teams |
|
Tracking protection |
Basic (cookies & permissions) |
Advanced tracker and ad blocking |
Not focused on blocking, but on identity separation |
|
Browser fingerprint control |
Minimal or none |
Limited (partial randomization) |
Full control (OS, fonts, WebGL, canvas, timezone, etc.) |
|
Profile isolation |
Basic user profiles |
Basic to moderate |
Advanced, each profile behaves like a separate device |
|
Multi-account support |
Risky at scale |
Safer than standard, but limited |
Designed specifically for large-scale multi-account use |
|
Proxy integration |
Manual, browser-wide |
Limited or external |
Built-in, per-profile proxy assignment |
|
Automation support |
Limited |
Very limited |
Strong (API, automation workflows, testing) |
|
Performance & compatibility |
Excellent website compatibility |
Very good, occasional site issues |
Very good, depends on configuration |
|
Ease of use |
Very easy |
Easy to moderate |
Moderate to advanced |
|
Common risks |
Tracking, data profiling |
Some sites may break |
Misuse if poorly configured |
|
Best use cases |
Browsing, work, entertainment |
Safer everyday browsing |
E-commerce, ads, social media, QA testing |
This expanded comparison shows why various types of browsers coexist instead of competing directly.
- Standard browsers focus on simplicity and performance.
- Privacy browsers prioritize user data protection.
- Antidetect browsers solve complex identity and scalability problems that other browsers are not designed to handle.
Understanding these differences makes it easier to choose the right browser based on how you use the internet, not just what websites you visit.
How to Choose the Right Browser for Your Needs
Choosing the right browser in 2026 depends on your priorities:
- If you want speed, compatibility, and convenience, a standard browser is sufficient.
- If privacy and reduced tracking matter most, a privacy-focused browser is a better fit.
- If you manage multiple accounts or require strict identity separation, an antidetect browser is essential.
Understanding what the different types of web browsers are helps users select the right tool instead of forcing one browser to handle tasks it was never designed for.
FAQ
1) Are privacy browsers better than regular browsers?
Privacy browsers are not inherently better for everyone. They offer stronger tracking protection, but regular browsers often provide better performance, compatibility, and ease of use for general tasks.
2) What makes an antidetect browser different?
Antidetect browsers actively control browser fingerprints and isolate environments. This allows multiple identities to function independently, which standard and privacy browsers cannot reliably achieve.
3) What are the top 5 popular web browsers?
As of 2026, the top 5 popular web browsers worldwide are:
1. Google Chrome
2. Safari
3. Microsoft Edge
4. Mozilla Firefox
5. Opera
Each of these belongs to a different segment of the broader browser landscape, reinforcing why understanding various types of browsers is increasingly important in the modern internet. If you tend to keep your browsing identity safe and manage multiple accounts for certain platforms, AdsPower is the best choice, which is trusted by 9M+ users.

People Also Read
- How to Fix ChatGPT Errors: Network, Message Stream & Access Issues

How to Fix ChatGPT Errors: Network, Message Stream & Access Issues
Fix ChatGPT errors caused by network drops, message stream breaks, and access issues. Use fast, practical steps to restore stable responses.
- How to Fix an IP Ban on Discord 2026?

How to Fix an IP Ban on Discord 2026?
Discord IP bans block your network access. This 2026 guide explains how to detect, recover, appeal, and prevent IP restrictions so you can reconnect
- How to Unblock TamilMV Safely and Access Tamil Movies Online (2026 Guide)

How to Unblock TamilMV Safely and Access Tamil Movies Online (2026 Guide)
Learn how to unblock TamilMV safely in 2026, access tamil movies mv, compare proxies, VPNs, and antidetect browsers for secure, stable online access.
- How to Download Reddit Videos in 2026: MP4, GIFs, and Images Made Easy

How to Download Reddit Videos in 2026: MP4, GIFs, and Images Made Easy
Learn how to easily and safely download Reddit videos, GIFs, and images in 2026. Step-by-step methods, troubleshooting tips, and best practices includ
- How Do You Make Money on Twitch in 2026? (Complete Guide)

How Do You Make Money on Twitch in 2026? (Complete Guide)
Learn how to make money on Twitch in 2026 with updated monetization methods, viewer tips, income strategies, and tools to help beginners and streamers


